If you are suffering with foot, leg or lower back problems, visit Hervey Bay and Maryborough's expert podiatry team
The foot has - 26 bones - 33 joints - 107 ligaments - 19 muscles
All these pieces work together to allow the foot to move in various ways while balancing your weight and propelling you forward or backward all day, every day. It's no wonder that most people will experience some kind of foot problem at some point in their lifetimes. The good news is, there are qualified professionals at Family Feet Podiatry ready to help.
Biomechanical Related
Heel Pain (Plantar fasciitis & Heel spurs)
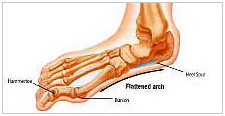
Flat feet
Severe’s Disease (Childhood heel pain)
Neuroma (Pain in the ball of the foot)
Achilles Tendonitis
Bunions
Arthritic feet
Ankle sprains and instability
Injuries
General Podiatry
Routine footcare
Corns & Callous
Ingrown toenails
Plantar warts
Fungal nails
Athlete’s foot
Hammer Toes
Diabetic footcare
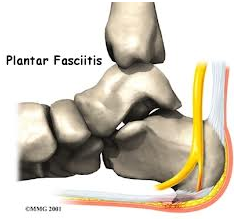
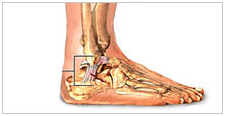
Plantar Fasciitis/Heel Spurs
This condition commonly results from inflammation of the band of fibrous connective tissue (fascia or "ligament") running in and along the arch of the foot, from the heel to the ball of the foot. The condition occurs when the plantar fascia is strained over time beyond its normal extension, causing the soft tissue fibres of the fascia to tear or stretch at points along its length. This commonly leads to inflammation, pain, and possibly the growth of a bone spur where it attaches to the heel bone. The condition is most often successfully treated with measures such as use of anti-inflammatory medications and ice packs, stretching exercises, and prescription orthotics devices.
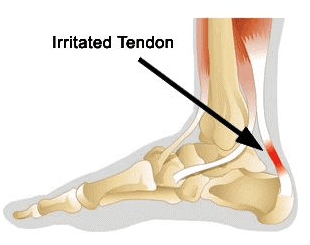
Achillies Tendonitis
The pain caused by achilles tendonitis can develop gradually without a history of trauma. Achilles tendonitis is aggravated by activities that repeatedly stress the tendon, causing inflammation. It is a common problem often experienced by athletes, particularly distance runners. The most common cause is over-pronation (flat feet). This occurs because the arch collapses upon weight bearing, adding stress on the achilles tendon. Other factors that lead to achilles tendonitis are improper shoe selection, inadequate stretching prior to engaging in athletics, a short achilles tendon, direct trauma (injury) to the tendon, and heel bone deformity.
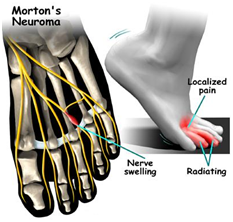
Neuroma
Neuromas are a painful condition, also referred to as a "pinched nerve" or a nerve tumor. It is a benign growth of nerve tissue frequently found between the third and fourth toes that bring on pain, a burning sensation, tingling, or numbness between the toes and in the ball of the foot. The principal symptom associated with a neuroma is pain between the toes while walking. Those suffering from the condition often find relief by stopping their walk, taking off their shoe, and rubbing the affected area. At times, the patient will describe the pain as similar to having a stone in his or her shoe. The vast majority of people who develop neuromas are women. There are many treatment options including orthotics that may alleviate your symptoms.
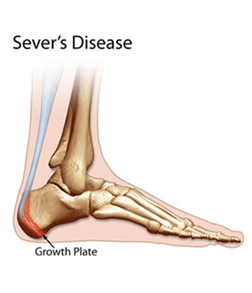
Sever’s Disease/Condition
The most prominent symptom of Sever's disease is heel pain. It is usually aggravated by physical activity such as walking, running or jumping. The pain is localised to the back and sides of the heel over the calcaneal apophysis (growth plate). Sometimes, the pain may be so severe that it may cause limping and interfere with physical performance in sports. The main diagnostic tool is pain on medial- lateral compression of the calcaneous in the area of growth plate. X-ray’s are usually normal. Therefore the diagnosis of Sever's disease is primarily clinical. It is most common in children 8-14 years of age, but can occur at any age until the growth plate has ossified.
Cause
Sever’s disease is directly related to excessive traction since the bones and tendons are still developing. It occurs more commonly in children who over-pronate (feet roll in), and involves both heels in more than half of patients. This is generally exacerbated when playing sports or anything that involves a lot of heel movement. It can be associated with starting a new sport, or the start of a new season.
Treatment
Treatment general involves the use of prescription orthotics to correct abnormal foot function and reduce torsional strain on the heel bone. This is normally done in conjunction with good footwear, stretching, ice and anti-inflammatory medication (severe cases).
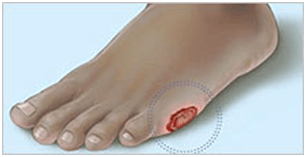
Bunions
Bunions are a bony bump on the first metatarsal bone, at the base of the big toe.
Cause
This portion of the foot bone becomes prominent when the first metatarsal and big toe shift out of alignment, most often as a result of tight shoes, genetics or excessive pronation (flat feet).
Treatment
Pain can be treated with prescription orthotics. Purchasing wide shoes can relieve pressure on the bump. Bunions can be corrected with a minor surgical procedure where the bump is removed and the bones are shifted back into alignment. This is done on an outpatient basis and usually people are able to walk on the foot that day and return to an athletic shoe within a few weeks.
Fungus Toenails
Nail fungus is a fungal infection in one or more of your nails. An infection with nail fungus may begin as a white or yellow spot under the tip of your fingernail or toenail. As the nail fungus spreads deeper into your nail, it may cause your nail to discolour, thicken and develop crumbling edges - an unsightly and potentially painful problem.
An infection with nail fungus may be difficult to treat, and it may recur. But medications (topical and oral) are available to help clear up nail fungus.
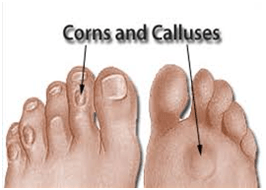
Corns and Calluses
These are areas of hard, dense skin. Calluses are wider and flatter and found on the soles of the feet. Corns are smaller and usually found on the tops of toes, or between them.
Cause
Too much pressure upon the skin causes Corns and calluses. The skin's response to this pressure is to grow thick and hard, creating the corn. Most corns are seen on the tops of contracted, hammered toes or frequently between toes. Here the knuckle is causing too much pressure, or sometimes, a spur between the toes projects out and creates the corn.
Treatment
There are a number of treatment options. Trimming the corn or callus and applying a felt or moleskin pad will give temporary relief. An orthotic support with a depression to relieve the pressure on the ball of the foot will help a callus. Purchasing wider shoes to decrease the pressure will help. Corns can be eliminated permanently if the toe is straightened and the pressure from the bone beneath the corn is eliminated.
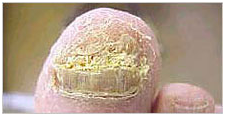
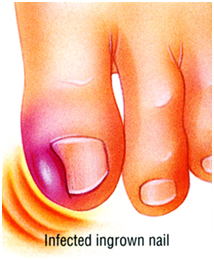
Ingrown Toenails
An ingrown nail is present when the side of the nail curves down into the flesh and causes pain, and frequently infection.
Cause
Ingrown nails often run in families or can be the result of an injury to the root cells at the base of the nail. Nail fungal infections make the nails more thick and curved and can also contribute to this condition.
Treatment
These can be treated temporarily or permanently. A wedge of nail can be removed from the ingrown portion to relieve the pressure and this usually makes the toe comfortable for a few months. However the ingrown nail frequently returns. For permanent relief, the toe is anesthetised with local anaesthesia. The ingrown portion of the nail is removed, leaving the top, flat part alone. Once the root cells are exposed, they are cauterised with a chemical so that the ingrown part will no longer grow back. People are usually able to return to normal activities immediately.
Diabetic Foot
Diabetes is a medical condition that effects many areas of the body including the feet, eyes, kidneys, nerves and arteries. Some of the more dangerous problems involve the feet. Problems that might be considered minor in non-diabetics, like thick nails, corns or callouses, are dangerous with diabetics. Some diabetics lose sensation in their feet so they can't feel if they have a problem. Diabetics are more prone to infections and ulcerations (forming holes through the skin). How significant is this? Approximately 86,000 amputations are performed each year on diabetics in America (American Public Health Association). Comprehensive podiatric care and good control of the diabetes is the best treatment for prevention of diabetic foot problems.
Cause
Diabetes causes heightened levels of sugar in the blood which goes on to effects many areas and tissues of the body. Nerves begin to lose their function, beginning in the toe tips. The arteries can become occluded (blocked) causing inadequate blood flow to the feet. Skin becomes dry, cracked and brittle. Corns, calluses and ingrown nails that put pressure on the skin can go on to cause infection and ulceration.
Treatment
Regular foot care is essential for prevention of diabetic complications, including testing for loss of sensation and ongoing education for home care. Debridement of corns, calluses, ingrown nails that could cause skin breakdown at regular intervals is essential. A prescription for protective shoes is given if necessary.
Hammertoes
Tendon imbalance is the major cause of toe deformities in adults. The tendons may stretch or tighten to compensate for imbalance of the foot. Thus, people with abnormally long toes, flat feet or high arches have a greater tendency to develop toe deformities. Over time, the toe may become permanently deformed and arthritic changes may develop. Patients can benefit from custom orthotics or may need surgery to alleviate the pain and deformity.
Injuries
There are many kinds of sports related injuries, some more prevalent due to the stresses of specific sports. Many injuries are caused by faulty foot structure and function and aggravated by improper shoes.
Treatment
The goal when treating athletes is to get them safely back to participating in their sports as soon as possible. If the condition is severe enough that they cannot participate in their sport for a period of time, an alternative exercise can usually be found to allow the athlete to stay in shape during the rehabilitation period. Once the painful condition has resolved, steps must be taken to prevent recurrence. If poor foot structure or function is to blame, we can often correct this with a support worn in the shoe. We offer both experience an d the latest technology in the fabrication of orthotic support.
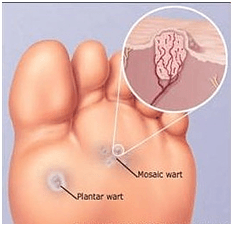
Plantar Warts
or Plantar Verrucae are caused by a virus that enters the body through a break in the skin. The virus grows in warm, moist environments. Plantar warts often spread to other areas of the foot, increase in size, and can form into a cluster. They may be difficult to distinguish from calluses. However, what differentiates them from a callus is that they have tiny black dots on the surface layer which are ends of capillary blood vessels. Plantar warts can be very painful and tender. Although plantar warts may eventually disappear by themselves, you should seek treatment if they are painful or to prevent spreading to other areas on your feet or other people.
Athletes Foot
Athlete's foot is a common infection caused by the tinea fungus. It is not serious. Symptoms include itching, burning and cracked, scaly skin between your toes. Tinea grows best in damp, dark and warm places, which is why it often develops between your toes. It can spread to your toenails, as well, making them thick and crumbly.
Advice
The expert team at Family Feet Podiatry can provide you with professional advice on how to maintain healthy feet. Certain exercises, hygiene treatments, devices and proper footwear can help prevent further problems with your feet.